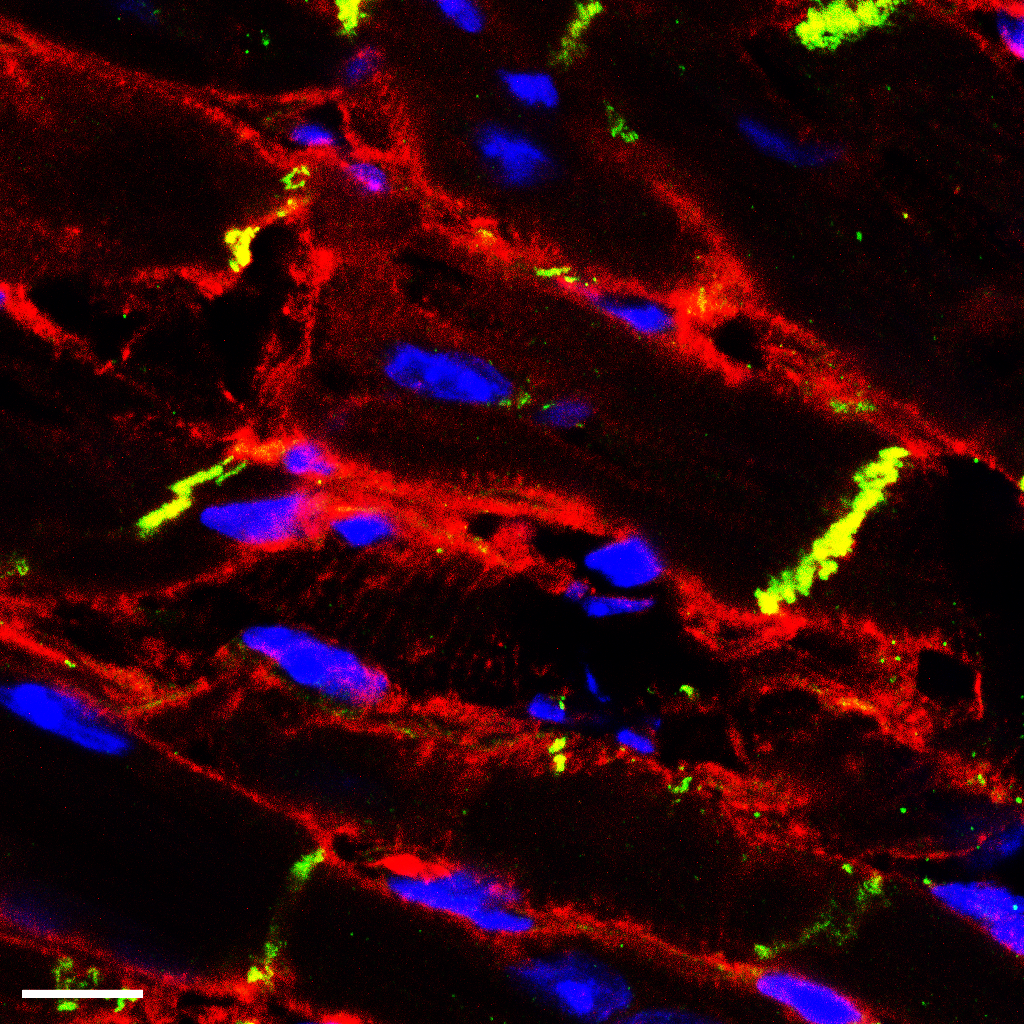
The Heart's Journey of maturation: The Epigenetic Architect Role of RNF20
- Author:Chia-Yeh Lin , Yao-Ming Chang , Hsin-Yi Tseng , Yen-Ling Shih , Hsiao-Hui Yeh , You-Rou Liao , Han-Hsuan Tang, Chia-Ling Hsu , Chien-Chang Chen , Yu-Ting Yan , Cheng-Fu Kao
- Journal: Cell Reports https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124723014286?via%3Dihub
Imagine our heart as a home under construction, with cardiomyocytes as the diligent builders. Scientists have long contemplated the blueprint guiding these builders in their tasks. Recently, a collaborative effort by Dr. Cheng-Fu Kao's team from the Institute of Cellular and Organismic Biology, along with Drs. Yao-Ming Chang, Chien-Chang Chen, and Yu-Ting Yen from the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, has uncovered a key player in this process: a protein named RNF20.
The critical construction phase for the heart 'house' spans the first three weeks of a mouse after birth. Without the presence of the epigenetic architect RNF20 during this phase, the heart cannot be built properly, putting the survival of the mice beyond eight weeks in jeopardy. Using a suite of advanced genomic analysis tools, the researchers meticulously tracked RNF20's orchestration of heart muscle maturation.
They discovered that RNF20's primary directive is to ensure the heart's structure is robust, similar to laying a solid foundation for a house. It then manages the cell growth cycle, akin to scheduling the work so that each heartbeat is strong and precise. RNF20's responsibilities go beyond that; it also oversees the metabolic pathways, ensuring the heart's utilities are up and running smoothly. What's even more intriguing is RNF20's role as an epigenetic regulator, adjusting the heart's internal space—by tightly winding or unwinding the DNA around proteins called histones—so each cardiomyocyte builder works optimally. RNF20's impact extends to reinforcing the connections between heart muscle cells (ID proteins). This meticulous organization is crucial for maintaining a stable heartbeat and is pivotal in preserving the heart's rhythmic harmony.
This landmark study not only positions RNF20 as an indispensable epigenetic regulator in heart development but also pioneers new avenues for treating heart conditions. The findings, published in 'Cell Reports', resonate with a global audience, offering fresh perspectives and hope for advancements in cardiac health and treatment.