Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants for Detection of COVID-19
- 作者:Ruei-Min Lu, Shih-Han Ko, Wan-Yu Chen, Yu-Ling Chang, Hsiu-Ting Lin and Han-Chung Wu
- 期刊: 本篇研究論文於2021年11月17日正式發表於《國際分子科學雜誌》 https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/22/12412
新冠病毒抗原快速篩檢試劑,中研院研發至取得 TFDA 緊急使用授權
新型冠狀病毒 RNA基因體不斷變異,在世界各地造成居高不下之疫情,如何大量而精確的檢驗受感染之病患,是科學家們持續發展檢測試劑之初衷。
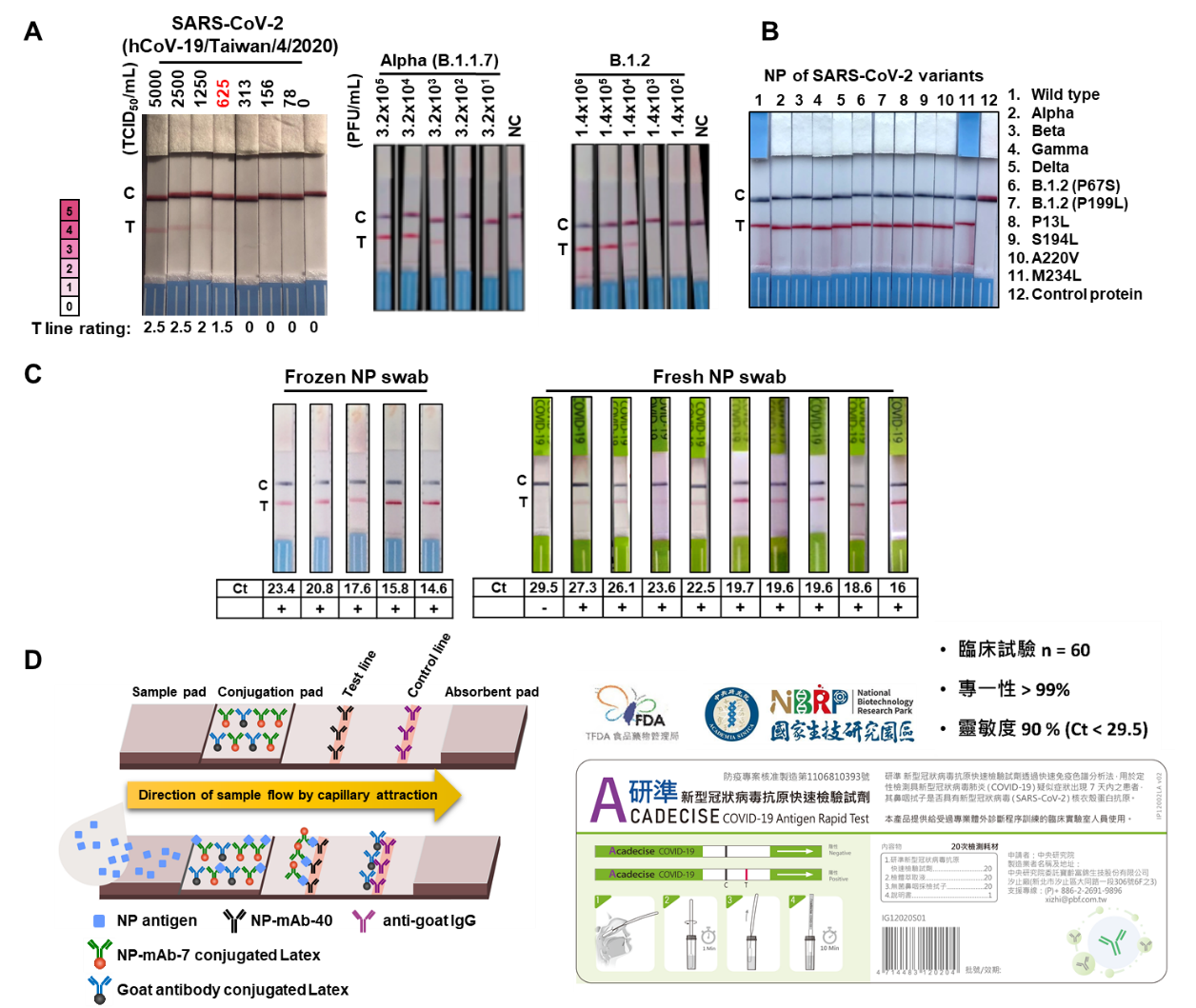
中研院細胞與個體生物研究所特聘研究員兼任生醫轉譯研究中心主任吳漢忠率領之研究團隊,利用側向流體免疫層析法 (LFIA) 建立新型冠狀病毒之抗原快速篩檢試劑,不需儀器輔助分析,只需15分鐘反應即判讀結果,適合運用於第一線大量篩檢以及醫療設備較不足地區。輔助醫療人員即時篩檢潛在感染者,避免疫情擴散。吳漢忠主任指出,由於新型冠狀病毒之核衣殼蛋白(Nucleocapsid, NP) 序列為高度保留區並具有高度免疫原之特性,團隊藉由小鼠融合瘤技術製備對抗NP之單株抗體,透過抗體配對分析,找出最佳組合運用於 LFIA 作為SARS-CoV-2 NP抗原之檢測。 其中以 NP-mAb-7 作為捕捉抗體接合乳膠粒子塗佈於膠金墊,並搭配測試線之檢測抗體NP-mAb-40,建構之快篩試劑 NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA,展現最佳之特異性與敏感性。NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA 對SARS-CoV-2原始病毒株的偵測極限為 625 TCID50/mL,對多種病毒變異株亦有辨識能力,包括 Alpha、B.1.2 與 Delta變異株等,與10 種以上 SARS-CoV-2 變異株之 NP 。
本篇論文第一作者,轉譯中心呂瑞旻研究助技師及專案經理柯釋涵博士表示,NP-mAb-7辨識之epitope位於NP之雙聚合區域 (dimerization domain) ,此區域相對穩定,發生突變機率較低,因此 NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA 對突變株之偵測敏感度較不容易受影響。研究團隊進一步分析特異性,NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA 不會交叉辨認 MERS-CoV 等5種人類冠狀病毒與20種常見人類呼吸道病原體,展現高度專一性。緊接著執行臨床試驗, 60 位招募者中有 10 位 RT-PCR核酸分子檢測為陽性檢體(Ct:16 - 29.5); 以 NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA 進行測試,顯示總體偵測準確率為 98.3%, 敏感度90%與特異性100% (Ct <29.5)。這些數據顯示 NP mAb-40/7 LFIA的偵測準確度具有臨床意義,因此於 2021 年 7 月8日取得台灣食藥署之COVID-19專案製造核准 (EUA),是中研院的第一例,此產品命名為「研準新冠病毒抗原快速篩檢試劑」(Acadecise COVID-19 antigen rapid test)。
吳主任指出除了運用抗原快速篩檢試劑做為早期感染之檢測外,另一方面,檢測血液中是否存在對抗新型冠狀病毒之抗體,也可以快速得知是否曾經遭受感染。特別的是分析IgG / IgM在血清抗體快篩試劑上出現的樣式,能夠依此推估判斷感染的時間先後,有助於疫情防堵與調查。因此其研究團隊在去年國際疫情爆發初期即著手與慈濟大學合作,完成新型冠狀病毒血清雙抗體IgG / IgM快速篩檢試劑之開發,於2020年7月27日獲得台灣食藥署之COVID-19專案製造核准。目前已完成運送19.5萬劑至醫療弱勢國家,如印尼、宏都拉斯、玻利維亞、多明尼加、聖露西亞,以及賴索托,進行公益人道救援,發揚Taiwan Is Helping之國際互助精神。
Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants for Detection of COVID-19
Ruei-Min Lu, Shih-Han Ko, Wan-Yu Chen, Yu-Ling Chang, Hsiu-Ting Lin and Han-Chung Wu
This paper was published in the International Journal of Molecular Science on November 17, 2021
Paper link: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/22/12412
The SARS-CoV-2 genome has a high mutation rate, which has led to the emergence of new variants and a continual state of emergency around the world. In order to identify infected individuals and bring the outbreak under control, scientists aspire to develop useful detection kits.
A research team led by Dr. Han-Chung Wu, a distinguished research fellow at ICOB and the director of BioTReC, has recently developed a new lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test. This test can give results within 15 minutes, and no instruments are required to read the outcome. It is especially suitable for first-line screening and for use in areas with limited access to medical equipment, allowing medical staff to quickly screen for potential infections and prevent spread of the virus. Dr. Wu indicated that the antigen detected by the test, the nucleocapsid protein (NP) of SARS-CoV-2, is a highly conserved viral component with prominent immunogenic characteristics. To develop the LFIA, the team first generated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against SARS-CoV-2 NP using mouse hybridoma technology. Then, they performed a screen to find the best pair of antibodies (NP-mAb-7 and NP-mAb-40) for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Based on this antibody pair, the test is called NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA. To construct the LFIA, NP-mAb-7 is utilized as a capture antibody linked to latex nanoparticles that are deposited on a conjugation pad. Meanwhile, NP-mAb-40 is immobilized on the test line, where it serves as a detection antibody. NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA showed high performance against the original virus, as it was able to detect wild-type SARS-CoV-2 at 625 TCID50/mL. In addition, the NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA can detect several variants, including Alpha, B.1.2, Delta, and more than 10 less well-known mutants of NP.
The capture antibody, NP-mAb-7, recognizes the dimerization domain of NP, which has a low mutation rate. Hence, NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA shows great promise and potential for detection of broad-spectrum SARS-CoV-2 variants, as suggested by the lead authors of this paper, Assistant Research Scientist Dr. Ruei-Min Lu and Project Manager Dr. Shih-Han Ko in BioTReC. The specificity of the test for SARS-CoV-2 was confirmed, as NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA did not cross-react with five other human coronaviruses or 20 common human respiratory pathogens. In clinical tests, a total of 60 swabs were evaluated, 10 of which were SARS-CoV-2-positive according to RT-PCR (Ct: 16-29.5). For these samples, NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA had an overall detection accuracy of 98.3%, with 90% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Based on the data from this clinical study, NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA was granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by TFDA on July 8, 2021, making it the first test from Academia Sinica to gain approval for use in the population (brand name: Acadecise COVID-19 antigen rapid test).
Notably, a different type of test, called a rapid serological antibody test, can be applied to characterize a patient’s infection history. These tests allow medical personnel to detect IgG and IgM against SARS-CoV-2 in the blood. Dr. Wu pointed out that the research team also began a cooperation with Tzu-Chi University at the beginning of the outbreak to develop serology tests for the detection of IgM and IgG against SARS-CoV-2. The test they developed was granted an EUA by TFDA on July 27, 2020. Up to now, 195,000 of these rapid serological antibody tests have been delivered to developing countries, such as Indonesia, Honduras, Bolivia, Dominican Republic, Saint Lucia, and Lesotho. The tests were distributed for the purpose of international humanitarian assistance and in the spirit of “Taiwan Is Helping”.